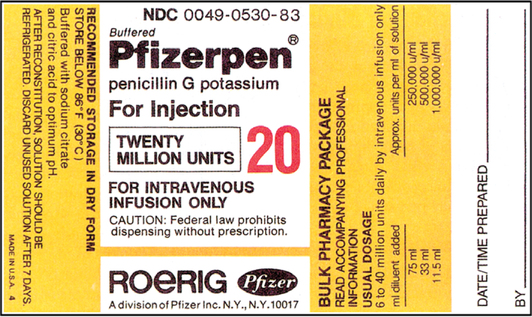
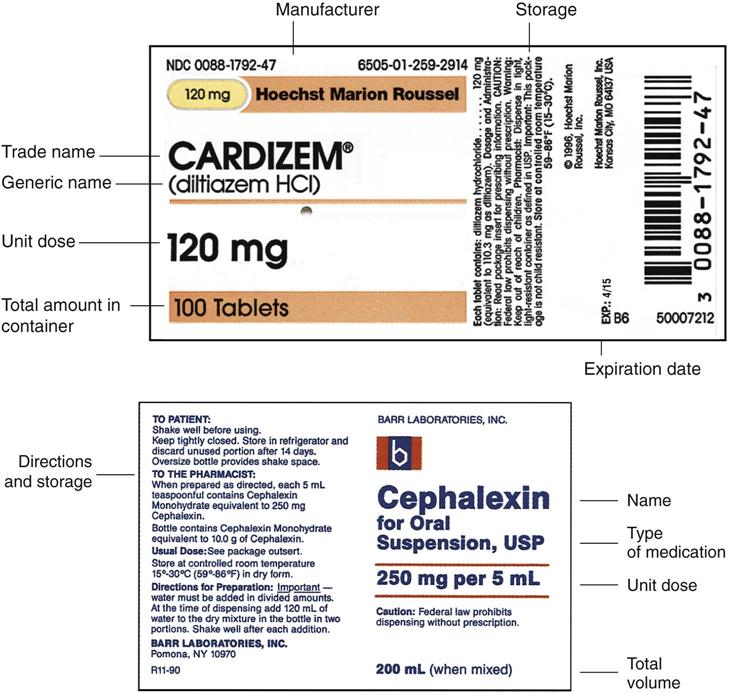
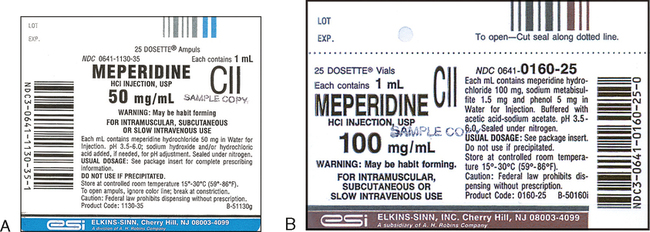
45 dosage calculations from medication labels
nurseslabs.com › preeclampsia-gestional6 Preeclampsia & Gestational Hypertensive Disorders Nursing ... Sep 09, 2022 · Decreased Cardiac Output. A decrease in circulating blood volume due to the shifting of fluid from the intravascular to the interstitial spaces occurs in a pregnant client with a hypertensive disorder due to the decrease of the circulating blood volume and the total vascular volume and an increase in the systemic vascular resistance, the heart rate decreases as well as the stroke volume. nurseslabs.com › bipolar-disorders-nursing-care-plans6 Bipolar Disorders Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs Mar 18, 2022 · Patient will respond to the medication within the therapeutic levels. Patient will sustain optimum health through medication management and therapeutic regimen. Patient will have stable cardiac status while in the hospital. Patient will drink 8 oz of fluid every hour throughout the day while on acutely manic stage.
› programs › veterinaryVet Tech Program Curriculum | Penn Foster The textbooks for this course are Medical Dosage Calculations and Essential Calculations for Veterinary Nurses and Technicians. This course will refer primarily to those resources. This course contains additional information and sample problems that pertain to the topics in your lessons, as well as highlights of important points from your ...
Dosage calculations from medication labels
› diptisorte › introduction-toIntroduction to pharmacology 1 - SlideShare Aug 23, 2018 · Drug Attachment • Medication chemically binds to specific sites called “receptor sites” – Agonist-chemical fits at receptor site well – Antagonist- a chemical blocks another chemical from getting to a receptor – Partial agonist - attach to the receptor but only produce a small effect Pharmacology AY 2013-2014 25 26. study.com › academy › lessonPharmacology Calculations & Conversions | Medical Math ... Jan 21, 2022 · These labels should be checked in accordance with the eight rights of administration to ensure that the administration route and dosage are correct before administering the medication. › math104 › lecture3Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage ... Tuberculin syringe: A tuberculin syringe is used to measure small doses, so it is often used to dose small children and infants.There are two different sizes of tuberculin syringes which you might encounter: one kind can hold a total of 1 mL, and another kind can hold a total of 0.5 mL; every hundredth of a mL is marked on a tuberculin syringe, and every fifth of a mL is labeled; this means ...
Dosage calculations from medication labels. basicmedicalkey.com › heparin-calculationsHeparin Calculations | Basicmedical Key Feb 11, 2017 · Therefore less than 1 mL will be needed to administer the dosage. This dosage can be measured accurately only with a tuberculin syringe (calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a milliliter). This dosage would not be rounded to the nearest tenth of a milliliter. A tuberculin syringe illustrating the dosage to be administered is shown in Figure 23-3. › math104 › lecture3Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage ... Tuberculin syringe: A tuberculin syringe is used to measure small doses, so it is often used to dose small children and infants.There are two different sizes of tuberculin syringes which you might encounter: one kind can hold a total of 1 mL, and another kind can hold a total of 0.5 mL; every hundredth of a mL is marked on a tuberculin syringe, and every fifth of a mL is labeled; this means ... study.com › academy › lessonPharmacology Calculations & Conversions | Medical Math ... Jan 21, 2022 · These labels should be checked in accordance with the eight rights of administration to ensure that the administration route and dosage are correct before administering the medication. › diptisorte › introduction-toIntroduction to pharmacology 1 - SlideShare Aug 23, 2018 · Drug Attachment • Medication chemically binds to specific sites called “receptor sites” – Agonist-chemical fits at receptor site well – Antagonist- a chemical blocks another chemical from getting to a receptor – Partial agonist - attach to the receptor but only produce a small effect Pharmacology AY 2013-2014 25 26.























.png)





Post a Comment for "45 dosage calculations from medication labels"